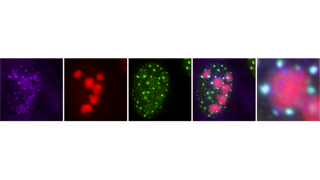
Glucose is not only a source of energy for muscles but also a building block required for muscle growth

Muscle cells use glucose as a building block for growth
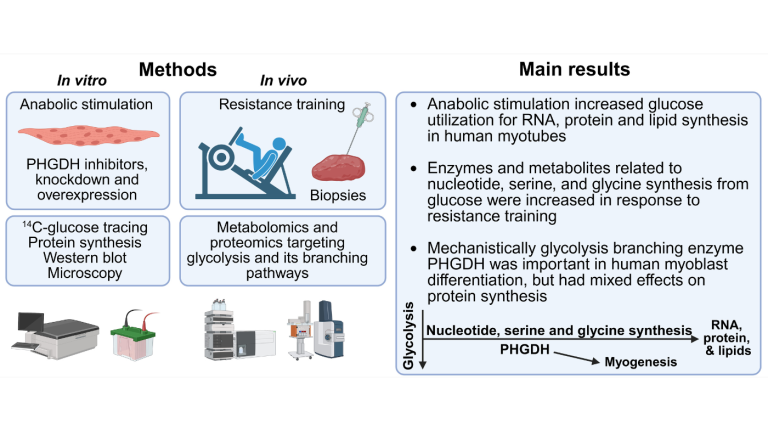
The study found that human muscle cells used glucose in laboratory conditions for the synthesis of proteins, RNA, and lipids. These are essential biomolecules needed for the structural components of muscle cells — and thereby for muscle growth. This was observed by using isotope‑labeled glucose and tracing the carbon atoms of the labeled glucose to the biomolecules. When muscle cell growth was stimulated, the utilization of glucose‑derived carbon atoms for the synthesis of proteins, RNA, and lipids increased.
The processes related to this phenomenon were also studied in the context of resistance training. It was found that resistance training increased the amounts of metabolites and enzymes required for the synthesis of glucose‑derived biomolecules in the muscles.
“It has long been thought that the role of glucose in muscles is mainly as fuel and as a building block for glycogen, a stored carbohydrate. However, my doctoral research shows that glucose can also be utilized in muscle cells as a building block for their growth”, says Doctoral Researcher Sakari Mäntyselkä.
“However, the results of the dissertation do not mean that excess glucose obtained through the diet would promote muscle growth”, Mäntyselkä clarifies.
The study also highlighted the role of the glycolysis branching pathway enzyme PHGDH in muscle cell growth and formation, which was further investigated in cultured human and mouse muscle cells. Doctoral research showed that the PHGDH enzyme appears to be particularly important in muscle fiber formation and may therefore have an important role in muscle damage repair.
– The results of my dissertation may prove valuable in developing drugs that enhance muscle repair or prevent muscle wasting, Mäntyselkä ponders.
(The infograph was created in https://BioRender.com)
The public examination of Sakari Mäntyselkä's doctoral dissertation in exercise physiology, entitled "Anabolic glucose metabolism in muscle—role of the serine synthesis pathway and mechanical loading," will be held on January 30, 2026, at 12:00 p.m. in Lecture Hall L304 of the Liikunta building. The opponent will be Senior Lecturer Brendan Gabriel (University of Aberdeen, UK), and the custos will be Professor Juha Hulmi (University of Jyväskylä). The language of the public defense will be English. At the end of the event, the audience may address any questions they may have to the custos.
The dissertation has been published as part of the University of Jyväskylä's JYU Dissertations series and is available online at: http://urn.fi/URN:ISBN:978-952-86-1242-1
The dissertation consists of the following publications:
I Mäntyselkä, S., Ahvenlammi, M., Vartiainen, J., Halonen, E. J., Kolari, K., Wackerhage, H., Permi, P., Varjosalo, M., Kelahaara, M. M., Ahtiainen, J. P., Kalenius, E., Kivelä, R., & Hulmi, J. J. (2025). Glycolytic metabolism and biomass production from glucose in human skeletal muscle growth. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 329(5), C1560–C1576. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00525.2025
II Mäntyselkä, S., Kolari, K., Baumert, P., Ylä-Outinen, L., Kuikka, L., Lahtonen, S., Permi, P., Wackerhage, H., Kalenius, E., Kivelä, R., & Hulmi, J. J. (2024). Serine synthesis pathway enzyme PHGDH is critical for muscle cell biomass, anabolic metabolism, and mTORC1 signaling. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 326(1), E73–E91. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00151.2023
III Mäntyselkä, S., Niemi, E., Ylä-Outinen, L., Kolari, K., Uusitalo-Kylmälä, L., Ortega-Alonso, A., Liimatainen, R-M., Fachada, V., Permi, P., Kalenius, E., Hulmi, J. J., & Kivelä, R. Mechanical loading induces distinct and shared responses in endothelial and muscle cells and reveals exercise-like molecular profiles. Submitted.The version submitted for peer review has been published as a preprint on bioRxiv: https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.06.27.661962
Background information:
Sakari Mäntyselkä graduated from High School (Kuopion klassillinen lukio) in 2014. He began his studies in biology at the University of Jyväskylä in 2016 and graduated with a Master of Science degree in cell and molecular biology in 2021. Sakari Mäntyselkä began working as a doctoral researcher in the Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences in 2022.
Further information:
Sakari Mäntyselkä, sakari.a.mantyselka@jyu.fi