High level research at the nanoscale
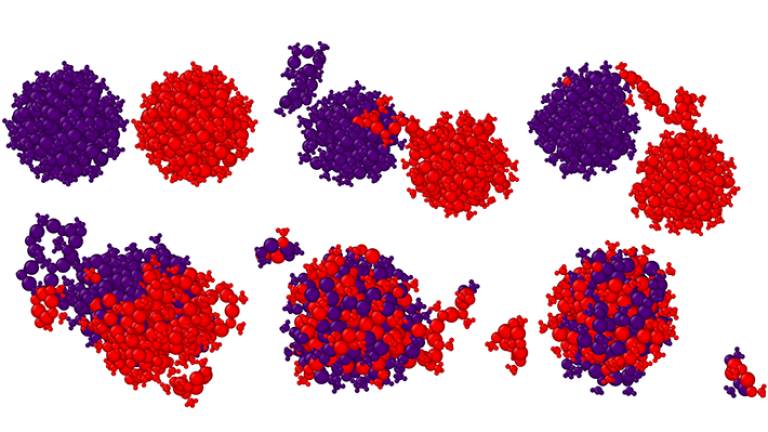
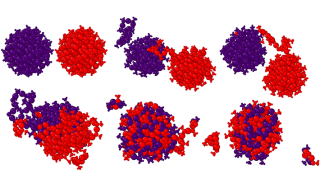
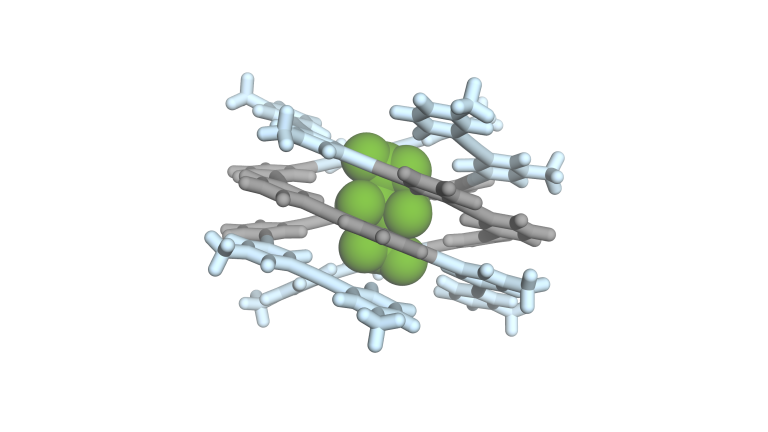
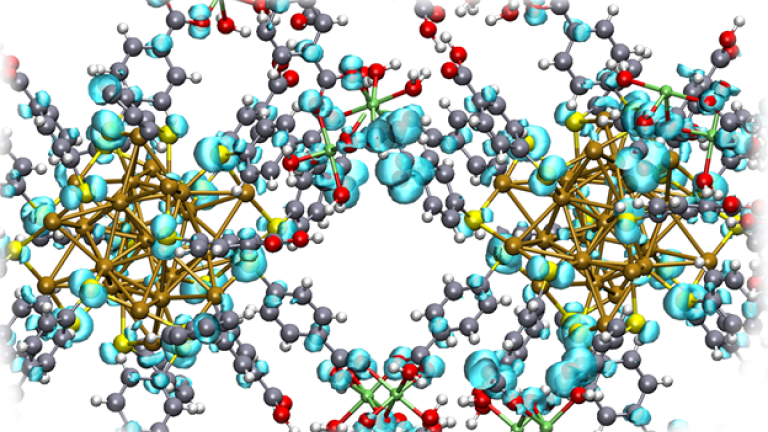
Researchers at University of Jyväskylä advance understanding of gold nanocluster behavior at elevated temperatures using machine learning-based simulations. These hybrid nanomaterials have promising applications in nanomedicine, bioimaging, and catalysis. They conducted ML-driven simulations extending up to 0.12 microseconds—achieving timescales five orders of magnitude longer than conventional quantum chemical methods allow—successfully capturing rare molecular events that would otherwise remain unobservable with such methods. Remarkably, the simulations captured two Au₁₄₄(SR)₆₀ clusters merging at 550 K, producing a larger cluster Au₂₃₉(SR)₆₉ with composition matching previously synthesized experimental results. This breakthrough opens new possibilities for rational design of nanomaterials with tailored properties for catalysis and other applications.
The research was published in Nature Communications. The publication was recognized as an Editors' Highlight in the Inorganic and Physical Chemistry section of Nature Communications.
Publication details:
Sabooni Asre Hazer, M., Malola, S. & Häkkinen, H. Thermal dynamics and coalescence of Au144(SR)60 clusters from a machine-learned potential. Nature Communications 17, 971 (2026)
DOI link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67700-w
More info, contact:
Maryam Sabooni: maryam.m.naderpour@jyu.fi